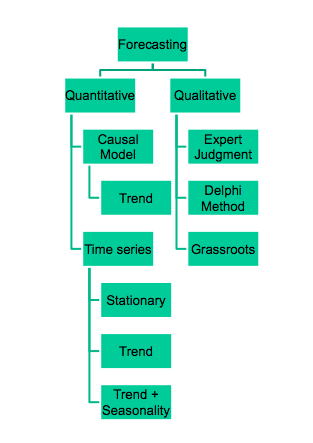
Forecasting prepares an organization for the future customer demands and potential lead times of raw material. This information gained from forecasting prepares the organization of costs associated on demand. Forecasting information could dictate staffing requirements and materials needed to be ordered in larger quantities.
The more reliable an organization’s process of forecasting is the more efficient and profitable the organization will be. Revenue and profit margins will increase as well as customer satisfaction. Furthermore, good forecasting improves the relationship and builds confidence that the customer will be taken care of. In turn, Customer satisfaction will retain customers and provide referrals to other potential customers.
“Seasonality is measured as a percentage or seasonal index of the average demand for a particular season, which is used to multiply the average value of the series.” Depending on the industry, there are several different seasonality situations that can be measured by the hour, day of week, monthly, or quarterly. A grocery store could measure the variable customers entering by the hour. This would give insight to personnel needed on hand to service and/or replenishment of products on the shelves.
“Control charts can effectively determine whether the variations present within a production system are natural, random, special-cause, or assignable variations that need to be explored further.”
“Cyclical factors are similar to seasonal factors but have a much longer time period and are often harder to identify.” Produce sales on specific commodities will fluctuate more due to the seasons between harvest and Mother Nature’s influence. Oregon, Idaho, Washington, Texas, and New Mexico each have their own onion season. Depending on the volume of the harvest, we could see the demand and price rise and fall depending on the crop’s yield.
When quantitative research is not available, this is when we need to resort to a qualitative method to forecast. Some of the most popular forecasting methods are through demographic research, the Delphi Method, and information from the sales team.
Demand and extrinsic and intrinsic methods are used during the process of utilizing data throughout the specific period we are trying to forecast. Intrinsic Forecast Method looks at the internal variables such as past sales. Extrinsic forecast focuses on outside influences/variables on the company’s product forecast/demand. Some of these outside influences can be as simple as start-ups, or season changes that effect customer demand.
Resources:
Boyer, K., & Verma, R. (2010). Operations & Supply Chain Management; for the 21st Century. Mason: South-Western, Cengage Learning.
Gilliland, M. (2012, July 13). The objectives of forecasting: narrow and broad. Retrieved from The Business Forecasting Deal: http://blogs.sas.com/content/forecasting/2012/07/13/the-objectives-of-forecasting-narrow-and-broad/
Kokemuller, N. (2015, April 10). Why Is Inventory Important for a Business? Retrieved from azcentral: http://yourbusiness.azcentral.com/inventory-important-business-2957.html
Planning & Forecasting. (2015, April 18). Retrieved from termwiki: http://en.termwiki.com/EN/extrinsic_forecast
Supply Chain Glossary. (2015, April 18). Retrieved from Demand Solutions: http://www.demandsolutions.com/resource-center/supply-chain-glossary/supply-chain-glossary-q/quantitative-forecasting-techniques.html